knee replacement
Highest level of proficient care is provided for all knee problems viz. Total knee replacement in Delhi.
Knee replacement surgery — also known as knee arthroplasty — can help relieve pain and restore function in severely diseased knee joints. The procedure involves cutting away damaged bone and cartilage from your thighbone, shinbone and kneecap and replacing it with an artificial joint (prosthesis) made of metal alloys, high-grade plastics and polymers.
In determining whether a knee replacement is right for you, an orthopedic surgeon assesses your knee's range of motion, stability and strength. X-rays help determine the extent of damage.
Your doctor can choose from a variety of knee replacement prostheses and surgical techniques, considering your age, weight, activity level, knee size and shape, and overall health.
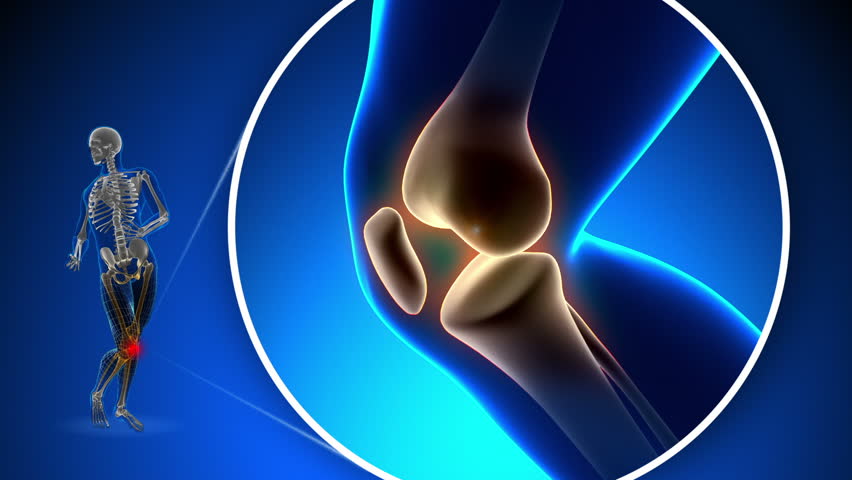
A total knee replacement is a surgical procedure whereby the diseased knee joint is replaced with artificial material. The knee is a hinge joint that provides motion at the point where the thigh meets the lower leg. The thighbone (or femur) abuts the large bone of the lower leg (tibia) at the knee joint. During a total knee replacement, the end of the femur bone is removed and replaced with a metal shell. The end of the lower leg bone (tibia) is also removed and replaced with a channelled plastic piece with a metal stem. Depending on the condition of the kneecap portion of the knee joint, a plastic "button" may also be added under the kneecap surface. The artificial components of a total knee replacement are referred to as the prosthesis.
The posterior cruciate ligament is a tissue that normally stabilizes each side of the knee joint so that the lower leg cannot slide backward in relation to the thighbone. In total knee replacement surgery, this ligament is either retained, sacrificed, or substituted by a polyethylene post. Each of these various designs of total knee replacement has its own particular benefits and risks.
A partial knee replacement surgery in Delhi to replace only one part of a damaged knee. It can replace either the inside (medial) part, the outside (lateral) part, or the kneecap part of the knee. Surgery to replace the whole knee joint is called total knee replacement.
Partial knee replacement surgery removes damaged tissue and bone in the knee joint. It is done when arthritis is present in only part of the knee. The areas are replaced with a man-made implant, called a prosthetic. The rest of your knee is preserved. Partial knee replacements are most often done with smaller incisions, so there is less recovery time.
Before surgery, you will be given medicine that blocks pain (anaesthesia). You will have one of two anaesthesia types: